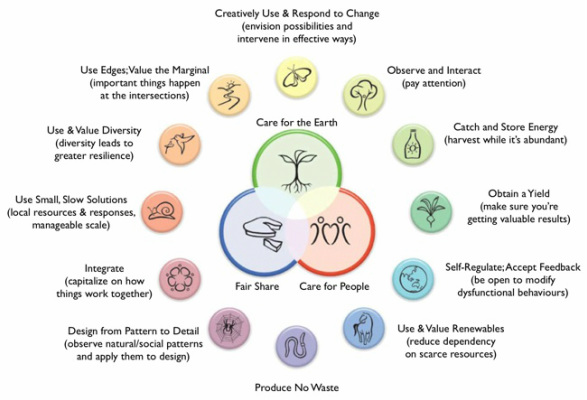
Permaculture as a systematic method was developed by Australians Bill Mollison and David Holmgren during the 1970s. The word "permaculture" originally referred to "permanent agriculture", but was expanded to also stand for "permanent culture" because a culture cannot survive over the long run without a sustainable agricultural system and land use ethic
.
Mollison has described permaculture as "a philosophy of working with, rather than against nature; of protracted and thoughtful observation rather than protracted and thoughtless labor; and of looking at plants and animals in all their functions, rather than treating any area as a single project system."
Permaculture draws from several other disciplines including organic farming, agroforestry, sustainable development, and applied ecology.
"The primary agenda of the movement has been to assist people to become more self reliant through the design and development of productive and sustainable gardens and farms. The design principles which are the conceptual foundation of permaculture were derived from the science of systems ecology and study of pre-industrial examples of sustainable land use."
Mollison has described permaculture as "a philosophy of working with, rather than against nature; of protracted and thoughtful observation rather than protracted and thoughtless labor; and of looking at plants and animals in all their functions, rather than treating any area as a single project system."
Permaculture draws from several other disciplines including organic farming, agroforestry, sustainable development, and applied ecology.
"The primary agenda of the movement has been to assist people to become more self reliant through the design and development of productive and sustainable gardens and farms. The design principles which are the conceptual foundation of permaculture were derived from the science of systems ecology and study of pre-industrial examples of sustainable land use."